Prostate surgery refers to a variety of surgical procedures performed to treat conditions affecting the prostate gland. The prostate is a walnut-sized gland located below the bladder and in front of the rectum in males. Common prostate conditions that may require surgery include benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), prostate cancer, and other prostate-related issues.
Here’s an overview of some common types of prostate surgery:
- Transurethral Resection of the Prostate (TURP):
- TURP is a surgical procedure used to treat benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), a condition characterized by the enlargement of the prostate gland.
- During TURP, a surgeon inserts a special instrument called a resectoscope through the urethra to reach the prostate gland. The resectoscope has a wire loop at the end, which is used to remove excess prostate tissue that is causing urinary obstruction.
- TURP is considered the gold standard treatment for moderate to severe BPH and can significantly improve urinary symptoms such as frequent urination, urgency, weak stream, and incomplete bladder emptying.
- Open Prostatectomy:
- Open prostatectomy is a surgical procedure used to remove a part or all of the prostate gland, typically in cases of very large prostates or when the gland is affected by cancer.
- During open prostatectomy, an incision is made in the lower abdomen or between the rectum and scrotum (perineum), and the prostate gland is carefully dissected and removed.
- Open prostatectomy may be performed as a traditional open surgery or as a minimally invasive procedure using robotic-assisted or laparoscopic techniques.
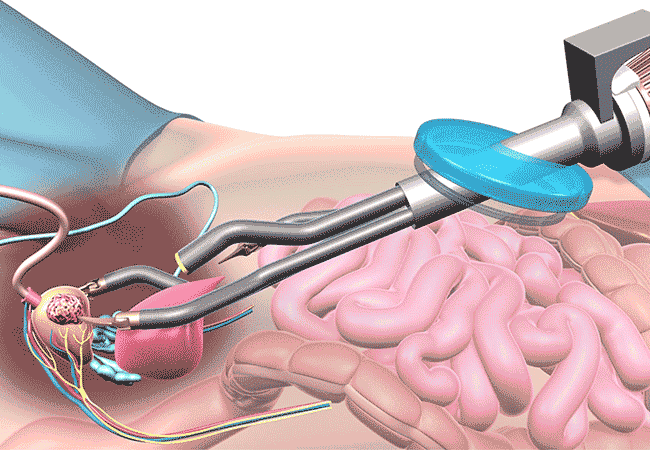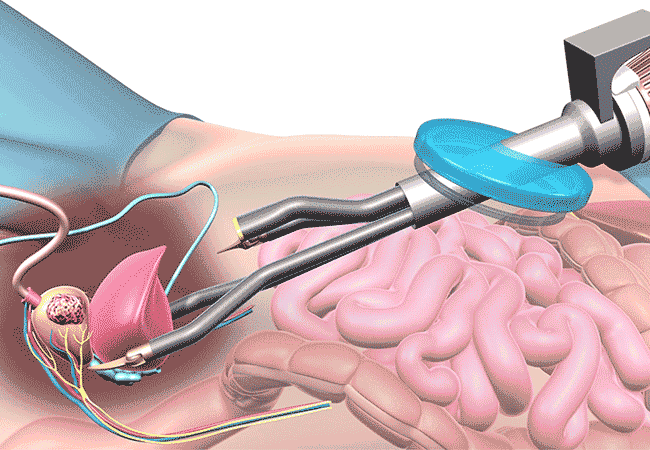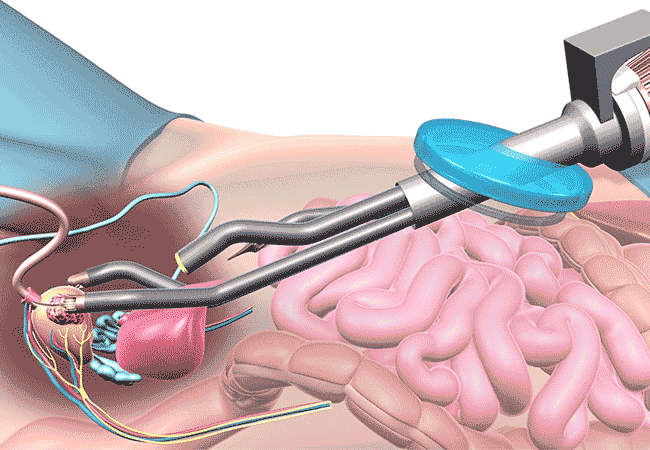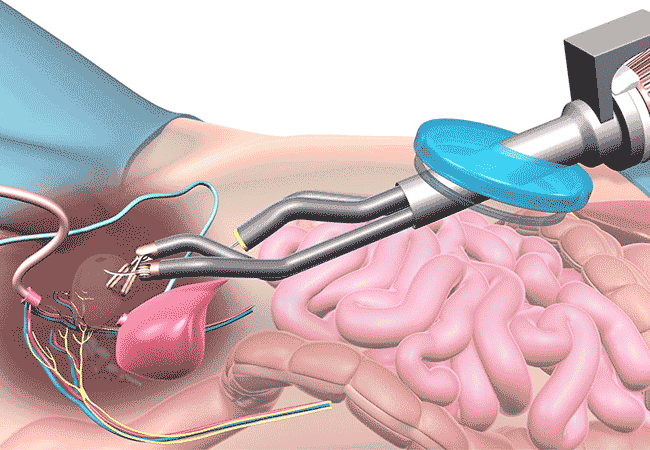
- Robot-Assisted Laparoscopic Prostatectomy:
- Robot-assisted laparoscopic prostatectomy, also known as da Vinci prostatectomy, is a minimally invasive surgical procedure used to remove the prostate gland in cases of localized prostate cancer.
- During this procedure, the surgeon uses a robotic system to control surgical instruments through small incisions in the abdomen. The robotic system provides enhanced visualization, precision, and dexterity compared to traditional laparoscopic surgery.
- Robot-assisted laparoscopic prostatectomy offers several advantages over open surgery, including smaller incisions, reduced blood loss, shorter hospital stays, and faster recovery times.
- Radical Prostatectomy:
- Radical prostatectomy is a surgical procedure used to remove the entire prostate gland along with surrounding tissues, such as seminal vesicles and nearby lymph nodes, in cases of localized prostate cancer.
- The goal of radical prostatectomy is to remove the cancerous tissue while preserving urinary and sexual function to the extent possible.
- Radical prostatectomy can be performed using various approaches, including open surgery, laparoscopic surgery, robot-assisted laparoscopic surgery, and nerve-sparing techniques to preserve erectile function.
- Transurethral Incision of the Prostate (TUIP):
- TUIP is a minimally invasive surgical procedure used to treat benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) in cases where the prostate gland is not significantly enlarged.
- During TUIP, small incisions are made in the prostate gland to widen the urethral opening and improve urinary flow. This procedure is less invasive than TURP and may be suitable for patients with smaller prostates or milder symptoms.
- Prostate Laser Surgery:
- Prostate laser surgery, including techniques such as laser vaporization (PVP) and laser enucleation (HoLEP), is a minimally invasive alternative to traditional surgical procedures for treating BPH.
- These procedures use laser energy to remove excess prostate tissue or vaporize prostate obstruction, resulting in improved urinary symptoms with less bleeding and faster recovery compared to traditional surgery.